RFID Applications areas
RFID Applications areas
Applications for RFID within the supply
chain can be found at multiple frequencies, and different RFID solutions
may be required to meet the varying needs of the marketplace.
Since UHF (Ultra High Frequency) has the range to cover portals and
dock-doors, it is gaining industry support as the frequency of choice
for inventory tracking applications, including pallets and cases.
|
|
|
RFID Tire Management System

In tire enterprises, the correct collection and
storage of tire production information plays an
important role in the control of tire production
process, quality inspection and quality tracking and
application. Although the current bar code technology
used to solve some of the problems, but in the actual
operation process, the production of information flow
before and after the disintegration of serious, can’t
meet the actual needs of the production line, and tire
quality testing failure, through the bar code is
difficult to quickly find fault Cause, resulting in a
huge waste of resources. RFID (radio frequency
identification) is a non-contact automatic
identification technology, which automatically
identifies the target through the RF signal and obtain
the relevant data, identification work without human
intervention, as a wireless version of bar code, RFID
technology with bar code does not have the waterproof,
Anti-magnetic, high temperature, long life, large
reading distance, the data on the label can be encrypted
and stored data capacity, etc., with the rapid flow of
information and fault traceability recognition function,
to meet the actual needs of the tire production line.
|
| | |
Books, Libraries, Archiving  60 case studies in section.
60 case studies in section.
|
|---|
| |
Financial, Security, Safety  233 case studies in section.
233 case studies in section.
|
|---|
| |
Healthcare  108 case studies in section.
108 case studies in section.
|
|---|
| |
Land and Sea Logistics, Postal  117 case studies in section.
117 case studies in section.
|
|---|
| |
Laundry  10 case studies in section.
10 case studies in section.
|
|---|
|
Leisure, Sports
209 case  studies
in section.
studies
in section. |
|---|
| |
Manufacturing  67 case studies in section.
67 case studies in section.
|
|---|
| |
Military  30 case studies in section.
30 case studies in section.
|
|---|
| |
Other  4 case studies in section.
4 case studies in section.
|
|---|
| |
Passenger Transport, Automotive  228 case studies in section.
228 case studies in section.
|
|---|
| |
| |
|
RAVIRAJ Technologies established in 2004, is dedicated
on manufacturing and providing rfid reader and rfid tags with high
performance and low cost. Our leading products are rfid labels, rfid
tags, smart card, rfid uhf reader, rfid handheld reader, rfid UHF
antennas.
Raido frequency identification technology, is a new generation
technology that has been widely used in our everyday life, such as
security control, library management system, no-stop parking solution,
logistic, jewelry management system, to enable item-level management,
inventory and asset control.
In view of this promising market, RAVIRAJ Technologies are promoting
more cost-effective rfid reader, rfid labels, rfid tags, rfid smart card
so as to contribute and promote this cutting-edge technology forward. We
believe, by lower cost of rfid reader and tags will greatly help
creating a intelligent life and people will benefit from convenience of
radio frequency identification technology.
As a manufacturer we are distributing our high performance and
cost-effective products worldwide. We develop products according to
customers? require, to ensure high quality performance and make our
reader and tags easily integrated to your system and solution. From
RAVIRAJ Technologies, you will find a trustworthy partner. And together
we can build a brilliant future by promoting rfid technology forward.
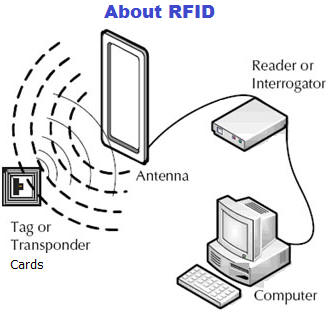
RFID tags are further broken down
into two categories:
- Active RFID Tags are battery
powered. They broadcast a signal to the reader and can transmit
over the greatest distances (100+ meters). Typically they can cost
$10?$50 or more and are used to track high value goods like vehicles
and large containers of goods. Shipboard containers are a good
example of an active RFID tag application.
- Passive RFID Tags do not
contain a battery. Instead, they draw their power from the radio
wave transmitted by the reader. The reader transmits a low power
radio signal through its antenna to the tag, which in turn receives
it through its own antenna to power the integrated circuit (chip).
The tag will briefly converse with the reader for verification and
the exchange of data. As a result, passive tags can transmit
information over shorter distances (typically 3 meters or less) than
active tags. They have a smaller memory capacity and are
considerably lower in cost (less than ?1), making them ideal for
tracking lower cost items.
There are two basic types of
chips available on RFID tags: Read-Only and Read-Write:
- Read-only chips are
programmed with unique information stored on them during the
manufacturing process?often referred to as a 'number plate'
application. The information on read-only chips can not be changed.
- With Read-Write chips, the
user can add information to the tag or write over existing
information when the tag is within range of the reader. Read-Write
chips are more expensive that Read-only chips. Applications for
these may include field service maintenance or 'item attendant
data'? where a maintenance record associated with a mechanical
component is stored and updated on a tag attached to the component.
Another method used is something called a "WORM" chip (Write Once
Read Many). It can be written once and then becomes Read-only
afterwards.

RFID Business Benefits
Use of RFID technology can increase
business productivity and reduce associated costs. To ensure that
companies benefit from the advantages RFID provides it is important
to understand how to adopt this technology. By analyzing current
practices and procedures eight main areas of benefit can be
identified. These are:
- Improved Productivity and Cost
Avoidance.
- Decreased Cycle Time and
Taking Costs Out.
- Reduced Rework.
- Reduced Business Risk &
Control of Assets.
- Improved Security and Service.
- Improved Utilization of
Resources.
- Increased Revenues.
- Exception Management.
Radio frequency identification is definitely
an enabling technology, which means it does not provide much
value on its own, but it enables companies to develop
applications that induce value. The web is yet another enabling
technology, and merely as the Internet enables companies to
speak, collaborate, educate, sell, entertain and distribute
products, RFID enables companies to do a variety of things. This
short article compares the major ways RFID is being used by
companies today to create value and also at some of the ways it
might be applied in the near future.
Keep in mind the RFID is used to identify objects or people. Its
advantages are that it requires no human intervention, tags can
usually be read even when a tag isn?t facing a reader antenna
(tags can not be go through metal plus some many other
materials), and also the information could be transmitted to
computers in real time. Typically, whenever a read reads a tag,
it passes three things to a number computer: the tag ID, the
reader?s own ID and also the time the tag was read. By knowing
which visitors by which locations, companies can know where a
method is, in addition to what it?s, and because of the time
stamp, they can know everywhere it has been.
NYK actively monitors containers
Asset Tracking
It?s no wonder that asset tracking is one of the most typical
uses of RFID. Companies can put RFID tags on assets that are
lost or stolen often, which are underutilized or that are just
hard to locate at the time they are needed. Pretty much every
kind of RFID system is employed for asset management. NYK
Logistics, a third-party logistics provider located in Secaucus,
N.J., required to track containers at its Long Beach, Calif.,
distribution center. It chose a real-time locating system that
uses active RFID beacons to discover container to within 10 feet
(subscribers, see Logistics Gets Cheaper through the Yard).
Air Canada is saving millions of dollars each year by tracking
food carts used at airports around the world. It chose to place
active transponders underneath the carts (passive tags were way
too hard to see around the metal carts) and readers on the
entrance and exits of catering facilities around the world
(subscribers, see Air Canada GETS Asset Tracking). It not just
loses fewer carts and spends less time and cash taking
inventory, it?s also able to better manage the movement of carts
so there are always carts at the airport catering stations that
need them.
RFID Journal has published case studies on other successful
applications, including El Paso County?s utilization of 915 MHz
passive tags to trace computers and IT and office equipment
(Tracking Assets from Prairie to Peak); law practice Fish &
Richardson P.C.?s use of 13.56 MHz tags to trace files (RFID
Brings Order to the Law); and a Singapore company?s use of 13.56
MHz technology to trace samples of construction concrete that
must be tested to ensure building safety (Tracking Concrete
Cubes for QA).
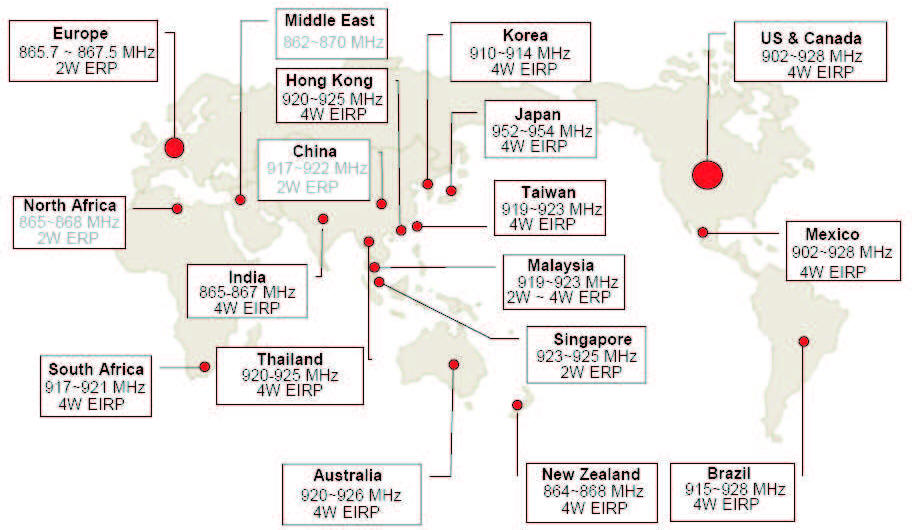
UHF (Ultra High Frequency)
Ultra High Frequency RFID operates between
902-928 MHz in North America and has read ranges up to
approximately 10ft. UHF has become the most used option in
Auto-ID applications due to its long read range and dropping
costs. UHF does have more issues with interference but a well
designed system can overcome these issues. UHF RFID is also well
suited to mounting on label stock making it the perfect
item/container level tag option.
Manufacturing
RFID has been utilized in manufacturing plants
for more than a decade. It?s used to track parts
and work in process and also to reduce defects,
increase throughput and manage the production of
different versions of the same product.
Johnson Controls, a Milwaukee, Wisc.-based
suppler of car and truck interiors, needs to
supply seats, dashboards along with other
components towards the big three automakers
where the automakers need it, when they need it.
Johnson Controls installed a 13.56 MHz system to
trace the different kinds of car and truck seats
it supplies. The machine has been proven as 99.9
percent accurate (subscribers, see Perfecting
Just-In-Time Production).
AM General?s Hummer
Boeing has been utilizing a 915 MHz system in
internet marketing Wichita, Kansas, facility to
track parts as they arrive, so that as they move
from one shop to a different within the
facility. In the past, barcode symbols related
to parts needed to be scanned manually when a
part visited a place where, say, it needed a
unique chemical treatment. It needed to be
scanned out again. If a part wasn?t scanned, the
organization lost track of it. Now RFID tags
track the movement of parts automatically,
reducing errors and the must have people search
for parts needed around the manufacturing line
(subscribers, see Boeing Finds the best Stuff).
AM General is applying an energetic RFID system
to trace parts bins on at its Hummer
manufacturing plant in Mishawaka, Ind. (RFID
Revs Up Hummer Plant). And Club Car made RFID an
integral part of its new golf buggy assembly
line and cut the time it takes to build each
vehicle?afrom 88 minutes to around 46
minutes?awhile ensuring that each car is built
to a precise specifications (Golf Car Maker
Scores with RFID).
Logistics Management
RFID technology has been used in closed loop
supply chains in order to automate parts of the
supply chain inside a company?s control for a
long time. A Procter & Gamble distribution
facility in Spain used a 13.56 MHz system to
improve throughput, reduce shipping errors and
cut labor costs (subscribers, see RFID Speeds
P&G Plant Throughput).
Paramount Farms, which processes about 60 % of
the U.S. pistachio crop and exports its products
to more than 20 countries, is depends on RFID to
assist automate the processing the incoming
shipments of pistachios from grower partners
(subscribers, see Farm Harvests RFID???s
Benefits).
As standards emerge, companies are increasingly
embracing RFID to trace shipments among supply
chain partners. Canus, a Canadian manufacturer
of skin care products made from goat?s milk, is
applying RFID to lessen the price of checking
shipments to the retail customers, and it?s
looking to use RFID temperature sensors to
monitor the health of products on the road (see
Soap Maker Cleans Up with RFID).
Retailing
Retailers for example Best Buy, Metro, Target,
Tesco and Wal-Mart have been in the forefront of
RFID adoption. These retailers are currently
focused on improving logistics efficiency and
ensuring method is on the shelf when customers
are interested it (see Wal-Mart Explains RFID
Roadmap).
Metro in Germany and Tesco in the United Kingdom
have done extensive testing to ascertain if
putting RFID tags on individual products in the
store can will help them to lessen from stocks.
And Hewlett-Packard is tagging printers and
electronic scanners shipped to Wal-Mart?s Texas
distribution centers. But given current tag
costs?a20 cents to 50 cents or more?ait?s likely
to be several years before RFID includes a big
effect on retailing.
Among the most discussed potential applications
would be the ability to automate the checkout
process and eliminate lines and the capability
to sell to consumers who opt in to loyalty
programs while they are making purchasing
decisions. Experts envision people putting items
right into a shopping cart software equipped
with a computer, small display and RFID reader.
When people who have opted into a loyalty
program put a steak into the cart, they might
have an ad for steak sauce or be told about wine
that?s on sale. When checking out, the consumer
walks via a tunnel reader, has every item in the
car read automatically and pays with the swipe
of contactless credit card. These applications
require tags to be on almost all components of
the store? something that won?t happen for at
least ten years.
RFID is catching on at turnstiles
Payment Systems
RFID is all the rage within the logistics world, however the
technology is also catching on like a convenient payment
mechanism. One of the most popular purposes of RFID today would
be to purchase road tolls without stopping. These active systems
have caught on in lots of countries, and quick service
restaurants are tinkering with utilizing the same active RFID
tags to pay for meals at drive-through windows.
RFID is also catching on like a convenient method to purchase
bus, subway and train rides. Boston, Washington, D.C., Seoul,
and many other cities are switching from magnetic stripe cards
to RFID cards because the RFID allows more and more people to
feed turnstiles fasters, reducing congestion, and the lack of
mechanical parts in readers reduces maintenance (subscribers,
see Smart Cards for Smart Commuters).
Many ski resorts in Europe use RFID lift tickets. In Japan,
consumers can download movie tickets to their mobile phones and
enter a theater by swiping an RFID tag in the phone past a
reader inside a turnstile. MasterCard and Visa are also
experimenting with RFID cards and key fobs for small payments
usually created using cash.
Security and Access Control
RFID has long been used being an electronic answer to control
who has access to offices or areas within office buildings. The
very first access control systems used low-frequency RFID tags.
Recently, vendors have introduced 13.56 MHz systems that offer
longer read range. The benefit of RFID is it works (a worker
holds up a badge to unlock a door, rather than looking for a key
or swiping a magnetic stripe card) and because there isn?t any
contact between the card and reader, there?s less wear and tear,
and therefore less maintenance.
RFID may also be accustomed to secure assets. Most late-model
cars come with an RFID reader in the steering column. A
transponder is baked into the plastic housing round the lower
key. The reader must receive the right ID from the key, or the
car won?t stop. This car immobilizer system has reduced auto
theft by 50 % because it has been around since Europe in 1994.
Active RFID tags can be coupled with motion sensors so that when
objects? as say, weapons kept in military depots? are moved
without authorization, a security is sounded. RFID tags may be
put on laptops and files containing sensitive documents to
ensure they aren?t removed from a building without
authorization.
An RFID bolt seal
After the terrorist attacks on Ny and Washington, D.C., in 2001,
the U.S. Department of transportation (DOT) conducted numerous
tests of RFID seals to safeguard containers. Becasue it is
impossible to check on each one of the millions of cargo
containers entering United States ports every year, the DOT
wishes to prevent terrorists sneaking weapons of mass
destruction into the Usa through the ports by putting an
electronic seal on each container.
Seals are active RFID tags that have a bolt or some other
mechanism for sealing a container. When the container is opened
without authorization, that details are communicated to some
computer next time the RFID tag in the seal is read. Then, an
alert could be sent and agents can check the container (see
Securing Your Cargo With Seals).
Other Applications
There are many other innovative ways to use RFID. One system
uses active tags in a bracelet to discover children at theme
parks (RFID Makes a Splash at Waterpark). Intel is promoting a
prototype system that will help people suffering from
Alzheimer?s disease to function more normally (RFID Aids
Alzheimer?s Patients). Brink?s, the security company, has
created a method in France that destroys bills when they get too
much from an RFID reader within an armored car (Brink?s Arms
Itself with RFID).
Wireless sensors represent the next stage beyond RFID. These may
be passive or active RFID tags which are coupled with
temperature loggers, motion sensors, radiation sensors and so
forth. The U.S. military is funding research into simple RFID
sensors that may detect pathogens in food. This can be employed
to protect the public against food-borne illnesses or perhaps
deliberate acts of terrorism.
Wireless sensors may also be tiny computers running their very
own operating system, have onboard sensors and communicate data
to one another. The NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena,
Calif., is working on a brand new generation of wireless sensor
networks. In early pilots, these have been accustomed to measure
soil and air temperatures, humidity and lightweight within the
MacAlpine Hills region of Antarctica; to gauge the movement of
water across a water recharge basin just west of Tucson, Ariz.,
to automatically turn on sprinklers in dry regions of the
Huntington Botanical Gardens in San Marino, Calif. (subscribers,
see NASA Creates Thinking RF Sensors).
As RFID technology evolves and diminishes expensive and much
more robust, the chances are companies and RFID vendors will
build up many new applications to solve common and different
business problems.

More information about RFID
http://www.rfid-product.com &
http://www.activewireless.com | |
:: Useful Links ::
Biometrics
Access Control
Fingerprint Scanners USB
Fingerprint technologies
Biometric Security
Embedded Resource
News
Biometrics Fingerprints Software
eOffice Resources
RFID Modem/Module
Biometrics Access control
OEM Fingerprint
Gold Campaign
Sensors
Software Development Kit
GSM GPRS Products
Biometrics services
Wireless Data Terminal
Biometric solutions
Biometrics Time Attendance
Rapidindex Electronics
Fingerprints Standalone Modules
Property Management
RFID
Info
Biometric Product
GSM GPRS Modem
Fingerprints Time Attendance
Electronics Healthcare
Wireless Security
Fingerprints Readers
Electronics
Time Attendance
Biometrics Tech
Fingerprint ID Products
Ayurvedic
Fingerprints Access Control
Time Recorders
Embedded Solution
Biometrics Resources
Mini ITX BOX
Electronics Connectors
 |
/
India, USA (New York, California), UK, Dubai, UAE, Oman,
Bahrain, Saudi Arabia, Australia, south Africa, Canada,
America, middle east, Europe, Asia, Argentina, Austria,
Azerbaijan, Bahamas, Bangladesh, Belgium, Bhutan,
Brazil, Brunei, Bulgaria, Burma, Cameroon, Canada, Chile,
China, Colombia. Congo, Costa Rica, Croatia, Cuba, Cyprus,
Czech Republic, Denmark, East west north south, Ecuador,
Egypt, England, c Laos, Malaysia, Maldives, Islands,
Mauritius, Mexico, Myanmar, Nepal, The Netherlands, New
Zealand, Nigeria, Ireland, Norway, Oman, Pakistan,
Philippines, Poland, Portugal, Qatar, Romania, Russia, Saudi
Arabia, Scotland, Seychelles, Sierra, Property
Singapore, South Africa, Spain, Sri Lanka, Sudan Sweden,
Switzerland, Syria, Taiwan, Tanzania,
impact components Thailand,
Trinidad, Tunisia, Turkey, United Arab
investments Emirates,
United Kingdom, Britain, United States of America,
Vatican, Venezuela, Vietnam, Wales, Zimbabwe |
 |
Ahmedabad, Agra, Allahabad, Amritsar, Aurangabad,
Bangalore, Baroda, Bhopal, Bhubaneshwar, Bikaner,
Calicut, Chennai (Madras), Chandigarh, Coimbatore,
Dehradun, Faridabad, Gandhinagar, Gwalior, Guwahati,
Hyderabad, Indore, Jaipur, Jalandhar, Jammu, Kanpur,
Kholapur, Kochi (Cochin), Kolkata (Calcutta), Lucknow,
Ludhiana, Mumbai (Bombay), Mysore, Nagpur, Nashik, New
Delhi, Patna, Pondicherry, Pune, Raipur, Rajkot, Ranchi,
Sangli, Sholapur, Shimla, Srinagar, Surat, Thane,
Trichi, Thiruvananthapuram (Trivandrum), Udaipur,
Vadodara, Varanasi, Vijayawada, Vishakhapatnam, Goa
Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Goa, Gujarat, Karnataka,
Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Orissa, Punjab, Rajasthan,
Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, Chandigarh, Delhi
ayurvedic
Devlopement, USB, Optical, cards, Sensors, Software
Biometrics Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Goa, Gujarat,
Karnataka, Biometric Madhya Pradesh, Biometrics
Maharashtra, Orissa, Punjab, Fingerprint Rajasthan,
Biometric Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, Biometric Chandigarh,
Delhi |
Home | Services
| Products
| Solutions
| Support
|
Partners |
Careers | Contact
Us |